MATEMATIKO MATH PRACTICE PROGRAM
FOR MATH PREPARATION CLASSES -- Middle School, GED, HiSET, TASC, ASVAB
OVERVIEW
Designed for teachers and students to offer extra practice in the basic skills. It can be used as an independent instructional tool in conjunction with a math text book such as the popular GED math manuals available at most bookstores. It is best used, however, as an instructional tool in GED, HiSET, and TASC preparation. It is also especially appropriate for ASVAB, Accuplacer, and middle school classes. Examples are generated by the program in a random fashion. This means that there are an unlimited number of unique examples generated. Another feature of the program is that when a student makes a mistake, the program will not allow a student to continue making mistakes until the problem is successfully corrected. In a classroom environment this encourages students to figure out the answer or to ask the teacher for help.
PROGRAM NOT AVAILABLE TO GENERAL PUBLIC AT THIS TIME:
Program does not include word problems at this time.
Should be used with a math book or manual. Click on BOOKS tabs above for suggested books for studying.
Includes over 100 modules.
Unlimited number of examples.
Developer is available to help users solve the examples via email.
Program will help users learn multiplication facts.
A checklist to measure progress is available on line.
MODULES
-
Learn Multiplication Tables – Fluency Mode
-
Learn Multiplication Tables – Practice Mode
-
Multiplication Tables – Test Mode
-
Learn Addition Tables – Fluency Mode
-
Learn Addition Tables – Practice Mode
-
Addition Tables – Test Mode
-
Learn Subtraction Tables – Fluency Mode
-
Learn Subtraction Tables – Practice Mode
-
Subtraction Tables – Test Mode
-
Learn Division Tables – Fluency Mode
-
Learn Division Tables – Practice Mode
-
Division – Test Mode
-
Basic Addition – no carry
-
Basic Addition – easy
-
Basic Addition – intermediate
-
Basic Addition – hard
-
Basic Addition – columns
-
Basic Subtraction – no borrow
-
Basic Subtraction – easy
-
Basic Subtraction – intermediate
-
Basic Subtraction – hard
-
Basic Subtraction – from zeros
-
Basic Multiplication – easy
-
Basic Multiplication – intermediate
-
Basic Multiplication – hard
-
Basic Multiplication – times ten
-
Basic Multiplication – times ten
-
Basic Division – easy
-
Basic Division – intermediate
-
Basic Division – hard
-
Basic Division – divide by ten
-
Average (mean)
-
Median
-
Reduce Fractions
-
Adding Fractions with Common Denominators
-
Adding Fractions with Different Denominators
-
Subtracting Fractions with Common Denominators
-
Subtracting Fractions with different Denominators
-
Multiplication of Fractions
-
Division of Fractions
-
Reduce Mixed Numbers
-
Addition of Mixed Numbers
-
Subtraction of Mixed Numbers
-
Multiplication of Mixed Numbers
-
Division of Mixed Numbers
-
Basic Decimal Addition – easy
-
Basic Decimal Addition – intermediate
-
Basic Decimal Addition – hard
-
Basic Decimal Subtraction – easy
-
Basic Decimal Subtraction – intermediate
-
Basic Decimal Subtraction – hard
-
Basic Decimal Multiplication – easy
-
Basic Decimal Multiplication – intermediate
-
Basic Decimal Multiplication – hard
-
Basic Decimal Multiplication – times ten
-
Basic Decimal Division – easy
-
Basic Decimal Division – intermediate
-
Basic Decimal Division – hard
-
Basic Decimal Division – by ten
-
Fractions to Decimals
-
Solve Proportions
-
Percents – find part
-
Percents – find whole
-
Percents – find percent
-
Percents – mixed types
-
Powers and Roots – basic powers
-
Powers and Roots – basic roots
-
Powers and Roots – advanced powers
-
Powers and Roots – advanced roots
-
Powers and Roots – third power
-
Probability Demonstration
-
Interest formula
-
Distance formula
-
Total Cost formula
-
Distributive Property
-
Order of Operations
-
Number Series
-
Simple Addition Equations
-
Simple Subtraction Equations
-
Mixed Addition and Subtraction Equations
-
Simple Multiplication Equations
-
Simple Division Equations
-
Mixed Multiplication and Division Equations
-
Simple Two-step Equations
-
Equations with Parentheses
-
Equations with Separated Unknowns
-
Add Signed Numbers
-
Subtract Signed Numbers
-
Multiply Signed Numbers
-
Divide Signed Numbers
-
Perimeter of Square
-
Area of Square
-
Perimeter of Rectangle
-
Area of Rectangle
-
Perimeter of Triangle
-
Area of Triangle
-
Area of Circle
-
Circumference of Circle
-
Pythagorean Relationship
-
Area of Parallelogram
-
Angles of Triangles
-
Angles formed by transversal of Parallel lines.
OVERVIEW OF LEARNING TABLES MODULES
There are three modes for learning tables: test mode, practice mode, and fluency mode. With each mode or menu selection, the learner can choose multiplication, division, addition, or subtraction. The test mode is an inventory of the 81 basic multiplication, addition, subtraction, and division facts. This is used to obtain a baseline and for students who already have a good mastery and wish to improve it. In the practice mode, the student chooses a table that he has a problem with for extra practice. The fluency mode is similar to the practice mode, but it encourages speed.
When a student has completed, he or she has the opportunity to review the results. A printed copy of the results can be made for the teachers records.
TABLES TEST MODE
This gives the student a baseline with which to compare progress.
Eighty-one basic examples (multiplication, subtraction, division, or
addition) are given in a random fashion. That is, no two tests will
have the examples in the same order.
When an example is answered correctly, the display is shown in blue.
When there is an error, the display turns red.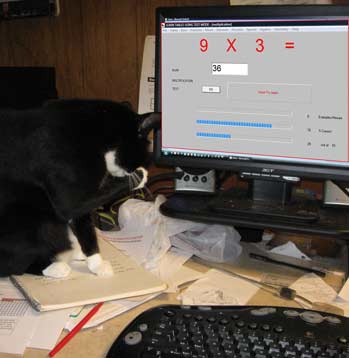
On the screen, a student sees three bars.
Progress bar shows number of examples completed.
Accuracy bar keeps a running tally of the percent of correct answers.
Speed bar indicates the speed the students are correctly completing the examples.
When completed, the student can print out the results. This includes the percent correct and the duration of the test. The printout also includes a bar graph showing which tables the student needs to work on in the practice or speed modes. In the picture on the right, Sarah, the cat, typed the wrong answer and is embarrassed. Notice that the speed bar indicates zero words per minute because for the last minute no answers were attempted.
TABLES PRACTICE MODE
It is used it to practice individual tables. For example, if the chart from the test indicates that a student needs practice with the nines tables. The student will select table nine and the number of examples desired. The developer usually instructs his students to select 50 examples. Fifty examples will then be randomly selected. There will naturally be repeats, but this will help learning.
When an example is answered correctly, the display is shown in blue.
When there is an error, the display turns red.
The bars found in the test mode above are also used in this mode:
Progress bar shows number of examples completed.
Accuracy bar keeps a running tally of the percent of correct answers.
Speed bar indicates the speed the students are correctly completing the examples.
When completed, the student can print out the results. This includes the percent correct. The printout also includes a bar graph showing which examples the student needs to work on in the practice or speed modes.
FLUENCY MODE
It encourages students to be quick when practicing. Students can determine how long he or she needs to complete each problem from 2 to 9 seconds. Students should be encouraged to use this mode to increase their speed and accuracy.
This mode works like the practice mode with a few differences. Like the practice test, the student will select a table he or she is having a problem with and like the others,
The figures remain blue if the answer is correct and
turn red when an error is made.
A feature unique to this mode is that after a delay ,selected by the student, the display turns green. The student can choose from one second to nine seconds. The object therefore is not only to come up with the correct response, but to come up with the correct response within the designated number of seconds.
A second difference between this mode and the practice mode is that when an example is answered correctly and accurately twice, it is not again displayed on the screen for the current session. This is similar to using a pack of flashcards. When a fact is learned, the card is taken out of the deck. When all the facts are learned, the deck is empty and the exercise is over.
PROBABILITY DEMO
It graphically shows the outcomes when one die or two dice are rolled ten million times. Can be used after students are given the opportunity to roll their own dice. Can be used with probability and ratio lessons. The developer gives each student two dice and graph paper to graph the results of rolling dice. The students’ results often look very much like the results on the computer screen The students learn that the results are more predictable when they are more rolls, e.g. ten million rolls. How long would it take a person to roll dice ten million times? How long does it take the computer?
WHOLE NUMBERS
Practice adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing whole numbers of varying levels of difficulty. Positive reinforcement is used. The student knows immediately if he is correct or not. If the example is incorrect, the screen text turns red. He is not allowed to continue until he has a correct answer. The student is given the opportunity to choose the number of examples and the level of difficulty. The number of examples correct the first time around is given at the end of the exercise.
Also special modules are included such as:
Adding and subtracting without regrouping. (Sometimes needed for
students with poor skills)
Subtracting where there are several 0 digits in the minuend.
(Many students need practice with this type of example.)Multiply by 10, 100. (To encourage students to do this type of
problem without pencil and paper)
DECIMALS
Practice adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing decimal numbers of varying levels of difficulty. Positive reinforcement is used. The student knows immediately if he is correct or not. If the example is incorrect, the screen text turns red. He is not allowed to continue until he has a correct answer. The student is given the opportunity to choose the number of examples and the level of difficulty. The number of examples correct the first time around is given at the end of the exercise.
This section includes fraction to decimal conversion. The student selects a denominator family. The example are given in order from smallest fraction to largest. For example if the 5 family is selected. The examples given will be 1/5, 2/5, 3/5 etc. This will help the students see the relationship between fractions and decimals. The instructor can use this to encourage students to memorize some families, such as the thirds and fourths.
The program runs on MICROSOFT WINDOWS. It is not available for other operating systems.
The program is shipped on one CD